Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
- Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(5):759-769. Published online October 5, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1515
- 3,182 View
- 192 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the long-term effects of diabetes drug costs on cardiovascular (CV) events and death.
Methods
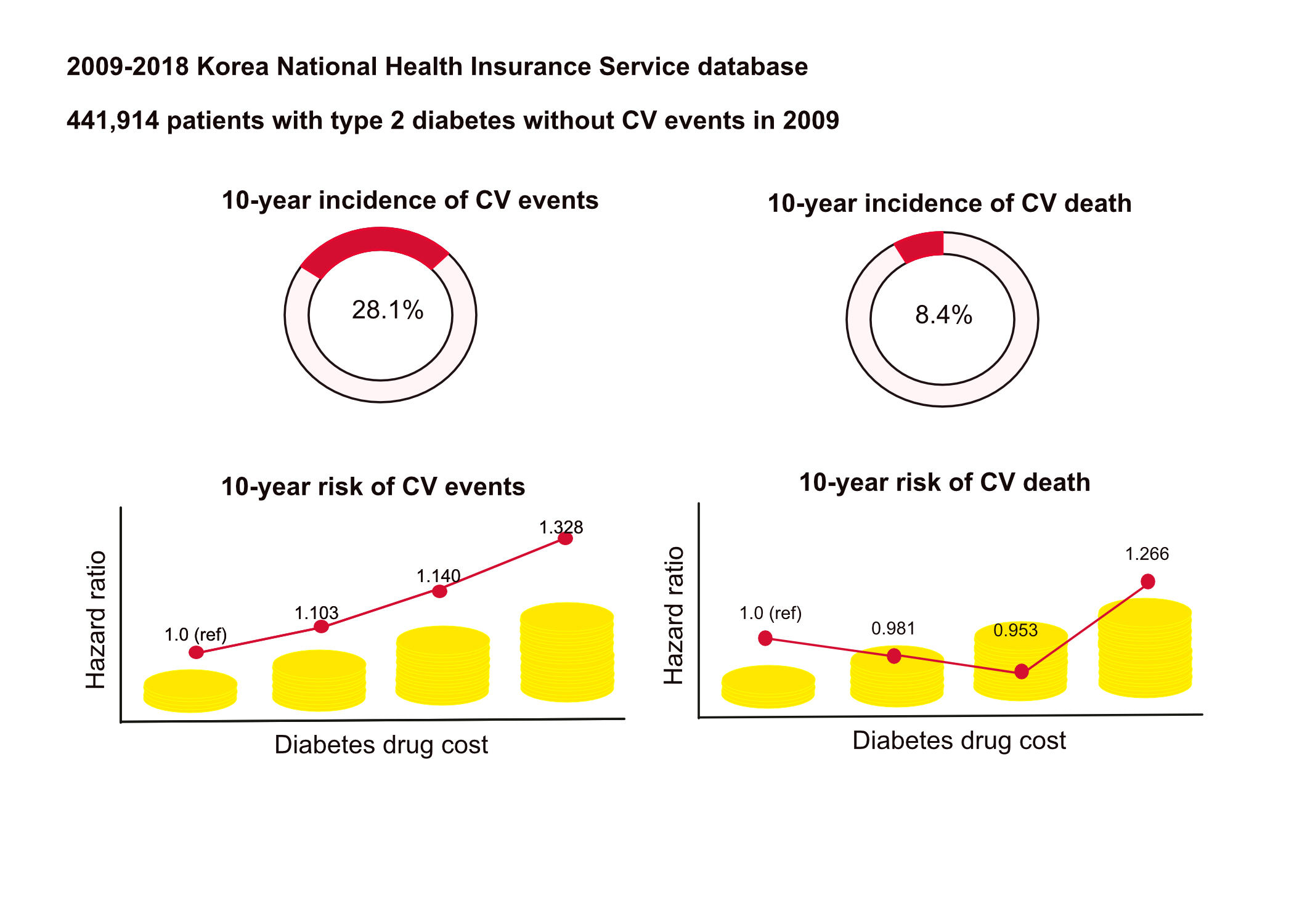
This retrospective observational study used data from 2009 to 2018 from the National Health Insurance in Korea. Among the patients with type 2 diabetes, those taking antidiabetic drugs and who did not have CV events until 2009 were included. Patients were divided into quartiles (Q1 [lowest]–4 [highest]) according to the 2009 diabetes drug cost. In addition, the 10-year incidences of CV events (non-fatal myocardial infarction, stroke, hospitalization for heart failure, and coronary revascularization) and CV death (death due to CV events) were analyzed.
Results
A total of 441,914 participants were enrolled (median age, 60 years; men, 57%). CV events and death occurred in 28.1% and 8.36% of the patients, respectively. The 10-year incidences of CV events and deaths increased from Q1 to 4. After adjusting for sex, age, income, type of diabetes drugs, comorbidities, and smoking and drinking status, the risk of CV events significantly increased according to the sequential order of the cost quartiles. In contrast, the risk of CV death showed a U-shaped pattern, which was the lowest in Q3 (hazard ratio [HR], 0.953; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.913 to 0.995) and the highest in Q4 (HR, 1.266; 95% CI, 1.213 to 1.321).
Conclusion
Diabetes drug expenditure affects 10-year CV events and mortality. Therefore, affording an appropriate diabetes drug cost at a similar risk of CV is an independent protective factor against CV death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of mental disorders on the risk of heart failure among Korean patients with diabetes: a cohort study

- Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism
Big Data Articles (National Health Insurance Service Database) - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
- Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
- Endocrinol Metab. 2022;37(3):466-474. Published online June 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2022.1440
- 3,898 View
- 138 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetes is a leading cause of death that is responsible for 1.6 million annual deaths worldwide. However, the life expectancy and age at death of people with diabetes have been a matter of debate.
Methods
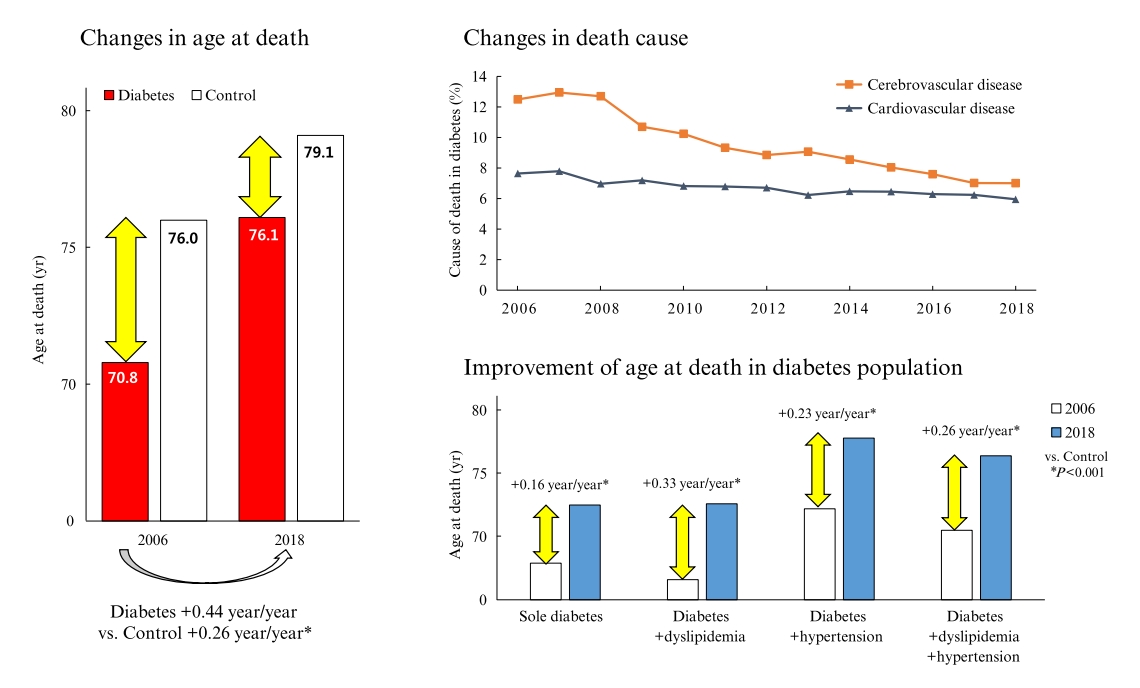
The National Health Insurance Service claims database, merged with death records from the National Statistical Information Service in Korea from 2006 to 2018, was analyzed.
Results
In total, 1,432,567 deaths were collected. The overall age at death increased by 0.44 and 0.26 year/year in the diabetes and control populations, respectively. The disparity in the mean age at death between the diabetes and control populations narrowed from 5.2 years in 2006 to 3.0 years in 2018 (p<0.001). In a subgroup analysis according to the presence of comorbid diseases, the number and proportion of deaths remained steady in the group with diabetes only, but steadily increased in the groups with diabetes combined with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension. Compared to the control population, the increase in the mean death age was higher in the population with diabetes. This trend was more prominent in the groups with dyslipidemia and/or hypertension than in the diabetes only group. Deaths from vascular disease and diabetes decreased, whereas deaths from cancer and pneumonia increased. The decline in the proportion of deaths from vascular disease was greater in the diabetes groups with hypertension and/or dyslipidemia than in the control population.
Conclusion
The age at death in the population with diabetes increased more steeply and reached a comparable level to those without diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study
Iee-Ho Choi, Sang-Woo Yeom, Sun-Young Kim, Jihye You, Jong-Seung Kim, Minsun Kim
Children.2023; 10(2): 358. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef
- Analysis of Cause-of-Death Mortality in Children and Young Adults with Diabetes: A Nationwide 10-Year Follow-Up Cohort Study

- Diabetes
- Comparison of Serum PCSK9 Levels in Subjects with Normoglycemia, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Impaired Glucose Tolerance
- Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Seong-Su Moon, Hochan Cho
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):480-483. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.480
- 4,953 View
- 115 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - We investigated proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) concentrations in individuals with normoglycemia, impaired fasting glucose (IFG), and impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). This was a pilot, cross-sectional study including 92 individuals who had not been diagnosed with or treated for diabetes. We measured PCSK9 levels in three groups of subjects; namely, normoglycemia (n=57), IFG (n=21), and IGT (n=14). Individuals with IFG and IGT showed higher PCSK9 concentrations than those in the normoglycemic group, with the highest serum PCSK9 concentrations found in individuals with IGT (55.25±15.29 ng/mL for normoglycemia, 63.47±17.78 ng/mL for IFG, 72.22±15.46 ng/mL for IGT, analysis of variance P=0.001). There were no significant differences in high- or low-density lipoprotein cholesterol among groups. Serum PCSK9 levels are increased in patients with prediabetes compared to subjects with normoglycemia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Emerging Insights on the Diverse Roles of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Chronic Liver Diseases: Cholesterol Metabolism and Beyond
Thomas Grewal, Christa Buechler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1070. CrossRef - Insight into the Evolving Role of PCSK9
Mateusz Maligłówka, Michał Kosowski, Marcin Hachuła, Marcin Cyrnek, Łukasz Bułdak, Marcin Basiak, Aleksandra Bołdys, Grzegorz Machnik, Rafał Jakub Bułdak, Bogusław Okopień
Metabolites.2022; 12(3): 256. CrossRef - Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) levels are not associated with severity of liver disease and are inversely related to cholesterol in a cohort of thirty eight patients with liver cirrhosis
Susanne Feder, Reiner Wiest, Thomas S. Weiss, Charalampos Aslanidis, Doris Schacherer, Sabrina Krautbauer, Gerhard Liebisch, Christa Buechler
Lipids in Health and Disease.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- Emerging Insights on the Diverse Roles of Proprotein Convertase Subtilisin/Kexin Type 9 (PCSK9) in Chronic Liver Diseases: Cholesterol Metabolism and Beyond

- Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
- Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Endocrinol Metab. 2017;32(2):274-280. Published online June 23, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2017.32.2.274
- 5,248 View
- 175 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although the beneficial effects of statin treatment in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis have been well studied, there is limited information regarding the renal effects of statins in diabetic nephropathy. We aimed to investigate whether, and which, statins affected renal function in Asian patients with diabetes.
Methods We enrolled 484 patients with diabetes who received statin treatment for more than 12 months. We included patients treated with moderate-intensity dose statin treatment (atorvastatin 10 to 20 mg/day or rosuvastatin 5 to 10 mg/day). The primary outcome was a change in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) during the 12-month statin treatment, and rapid renal decline was defined as a >3% reduction in eGFR in a 1-year period.
Results In both statin treatment groups, patients showed improved serum lipid levels and significantly reduced eGFRs (from 80.3 to 78.8 mL/min/1.73 m2 for atorvastatin [
P =0.012], from 79.1 to 76.1 mL/min/1.73 m2 for rosuvastatin [P =0.001]). A more rapid eGFR decline was observed in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group (48.7% vs. 38.6%,P =0.029). Multiple logistic regression analyses demonstrated more rapid renal function loss in the rosuvastatin group than in the atorvastatin group after adjustment for other confounding factors (odds ratio, 1.60; 95% confidence interval, 1.06 to 2.42).Conclusion These results suggest that a moderate-intensity dose of atorvastatin has fewer detrimental effects on renal function than that of rosuvastatin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial
Chan Joo Lee, Woong Chol Kang, Sang Hyun Ihm, Il Suk Sohn, Jong Shin Woo, Jin Won Kim, Soon Jun Hong, Jung Hyun Choi, Jung‐Won Suh, Jae‐Bin Seo, Joon‐Hyung Doh, Jung‐Woo Son, Jae‐Hyeong Park, Ju‐Hee Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jung Ho Heo, Jinho Shin, Seok‐Min
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2024; 26(3): 262. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic, anti-hyperlipidemic, and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug Guggulutiktaka ghrita on high-fat diet-induced obese rats
Samreen M. Sheik, Pugazhandhi Bakthavatchalam, Revathi P. Shenoy, Basavaraj S. Hadapad, Deepak Nayak M, Monalisa Biswas, Varashree Bolar Suryakanth
Journal of Ayurveda and Integrative Medicine.2022; 13(3): 100583. CrossRef - The challenge of reducing residual cardiovascular risk in patients with chronic kidney disease
Stefan Mark Nidorf
European Heart Journal.2022; 43(46): 4845. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease in Older People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Improving Prevention and Treatment Options
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Drugs & Aging.2020; 37(8): 567. CrossRef - Intracellular Mechanism of Rosuvastatin-Induced Decrease in Mature hERG Protein Expression on Membrane
Pan-Feng Feng, Bo Zhang, Lei Zhao, Qing Fang, Yan Liu, Jun-Nan Wang, Xue-Qi Xu, Hui Xue, Yang Li, Cai-Chuan Yan, Xin Zhao, Bao-Xin Li
Molecular Pharmaceutics.2019; 16(4): 1477. CrossRef - The problem of safety of lipid-lowering therapy
M V. Zykov
Kardiologiia.2019; 59(5S): 13. CrossRef - Regional evidence and international recommendations to guide lipid management in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes with special reference to renal dysfunction
Titus WL Lau, Kevin E.K. Tan, Jason C.J. Choo, Tsun‐Gun Ng, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Juliana C.N. Chan
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(3): 200. CrossRef - Lipids: a personal view of the past decade
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P Mikhailidis
Hormones.2018; 17(4): 461. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of combination therapy with telmisartan, rosuvastatin, and ezetimibe in patients with dyslipidemia and hypertension: A randomized, double‐blind, multicenter, therapeutic confirmatory, phase III clinical trial


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



